field permeability test in borehole|falling head permeability test astm : manufacture 1.1 This guide covers an integral part of a series of standards that are being prepared on the in situ determination of hydraulic properties of aquifer systems by single- or multiple-well tests. This guide provides guidance for development of a conceptual model of a field site and selection of an analytical test method for determination of hydraulic properties.
web15 de jul. de 2022 · Don't get me wrong the minx x300 is a solid sub with great performance for something so petite and little - but it can't rumble like a SVS SB1000.. no way in hell. Personally, i'd never pay the asking price of $1200-1400 AUD for a Minx301, but $100 AUD for the minx300 is a steal.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 30 de dez. de 2021 · Habemus Acústico MTV do Charlie Brown Jr. no YouTube, na íntegra e remasterizado em 4K! Um fã chamado Matheus .
The dimensions and geometry of the ‘test section’ have a key influence on flow conditions during the test and hence on the assessed permeability. For a falling head test (Figure 12.7a), water is rapidly added to raise the water level in the . 1.1 This test method covers field measurement of hydraulic conductivity (also referred to as coefficient of permeability) of porous materials using a cased borehole . Water permeability test in borehole without packer Part 3. Water pressure test in rock Part 4. Pumping tests Part 5. Infiltrometer tests Part 6. Closed packer systems The new standards use similar methods of analysis to .An open hole was left at the base of the borehole to allow for water seepage into the fractured rocks. As described in Eid (2007), the permeability coefficient (K) was calculated from the .
Field Testing Procedures for the Soil Permeability Coefficient For higher permeability stratified soils above 10^-3 cm/s, in-situ borehole methods suit site scale subsurface variability using packer injections isolating test zones .
1.1 This guide covers an integral part of a series of standards that are being prepared on the in situ determination of hydraulic properties of aquifer systems by single- or multiple-well tests. This guide provides guidance for development of a conceptual model of a field site and selection of an analytical test method for determination of hydraulic properties.Several sets of values are available for the shape factor of the cylindrical injection zone used to perform a field permeability test. Depending on the selected value, the resulting difference for hydraulic conductivity may reach 40% for long intake zones, and more than 100% for short intake zones. The commonly used shape factor is that given by Hvorslev (1951). Seven other factors .
custom nachi moisture meter site www.nachi.org
It is a valid test for soils with a high rate of flow like sands and gravels, but also some clay soils. Falling Head Test allows the head to decrease as water infiltrates the sample, diminishing the pressure over the course of the test. Falling head methods are generally limited to fine-grained soils. Soil Permeability Testing Equipment
Soil permeability, also termed hydraulic conductivity, is measured using several methods that include constant and falling head laboratory tests on intact or reconstituted specimens. Alternatively, permeability may be measured in the field using insitu borehole permeability testing (e.g. [2]), and field pumping tests.IN-SITU PERMEABILITY TEST PART 2 TESTS IN BEDROCK (Second Revision) 1 SCOPE This standard (Part 2) lays down recommendations for performing the pumping in permeability test, in which water is pumped under pressure into the test section, of bedrock through drill holes, wherein the sides of the hole do not collapse during the period of . The test consists first of all in making a cylindrical borehole to the depth where the permeability is to be measured [15], then in introducing a watertight tube to the roof of the cavity where .
Keywords Field permeability test . For the test in a well pipe, water seeps through the well screen with an artificial or natural filter zone around the screen (Zhang et al. 2019). The manipulation and interpretation of the field permeability test have been included in several textbooks (Cassan 1980, 2005; Monnet 2015) .
In-situ permeability testing should be carried out in accordance with the various parts of BS EN ISO 22282. It is important that the correct test is carried out as the tests are often limited to a particular situation and in particular to a limited range of permeabilites. . ISO 22476-7:2012 Field testing — Part 7: Borehole jack test; Up . Borehole investigations allow practitioners to determine the nature and location of the different soil/rock layers, collect samples, carry out in situ tests and permeability tests, and, if necessary, install piezometers and other subsurface monitoring tools. The location of the boreholes is chosen depending on the objective of the project and . 1.1 This test method covers field measurement of hydraulic conductivity (also referred to as coefficient of permeability) of porous materials using a cased borehole technique.When isotropic conditions can be assumed and a flush borehole is employed, the method yields the hydraulic conductivity of the porous material.The permeability property of the soil is required to facilitate the selection, design and specification of optimised soakwell and drainage systems. CMW conduct this test in boreholes drilled on site as part of the geotechnical site investigation. As the test is conducted in situ the site conditions are assessed with minimal disturbance compared .
The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily to. determine the suitability of sands and gravels for drainage purposes, and is made only on .The test results and derived permeability values from packer permeability tests in rock are affected by many factors - the host rock, the borehole and any associated zone of disturbance, water quality (injected water and water in the .
Typical setup of a cased borehole test in a compacted clay liner. Semilog plot of falling-head test. Datum and assumed piezometric level at top of compacted clay liner (see data in Table 1).field testing of borehole intervals were used to determine the water and air permeabilities of the uppermost unit of the BOREH0L8 SEI' Y . correlated to borehole air permeability (r=0.372), shown as Figure 3(d), but the geometric means of the data sets are not significantly different. The best overall correlation existsBelow listed are the field methods to determine permeability. Pumping out of wells. Pumping into wells. Constant Head Permeability Test (Constant Head Permeameter Test) . To perform the pumping-out test, a well needs to be penetrated into the soil stratum. The water table in the well will initially remain horizontal. But when water is pumped . Abstract. Pressure transducers (PTs) and an atmospheric pressure transducer (APT) were used to register test data during two types of permeability tests, which were performed in 14 wells monitoring a confined aquifer installed in the lab, and a field rising-head test in clay. The constant-head tests were performed using a peristaltic pump and thus .
The performance of clayey liners and covers is assessed by several methods including borehole variable-head permeability (k) tests. Different interpretations of the end-of-casing and Lefranc tests are discussed. In Quebec, most tests have been interpreted using the velocity-graph method. Its equations are presented and differences are illustrated by .Insitu Permeability Tests - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document discusses methods for conducting in situ permeability tests in boreholes to estimate the permeability of soils surrounding the borehole. It describes three common types of in situ permeability tests: 1) rising, falling, and constant head tests in boreholes, 2) in situ .In the case of the latter, the use of pulse testing to obtain directional permeability and storage parameters is also presented. The work follows current trends in petroleum well testing but adapted for geotechnical engineering. KEYWORDS: Permeability, hydraulic conductivity, fluid pressure, field testing. 1 INTRODUCTION
custom natal mahogany plant moisture meter guide
4. Pumping test • The purpose of pumping test is to get the information of permeability; • Pumping test is the active way to get k, the permeability. The passive way is to do the percolation test. • The principle of a pumping test is that if we pump water from a well and measure the discharge of the well and the drawdown in the well and in piezometers at known .
The permeability test is carried out on a cylindrical test specimen that is either confined laterally by a rigid container or by a flexible membrane. The specimen is subjected to differential hydraulic head and the water flow is measured under either a constant or falling head.
This study employs a simple permeameter constructed from a stainless-steel standpipe (diameter: 6.3 cm, thickness: 0.1 cm, and length: 120 cm for laboratory test, 150 cm for field test).Several sets of values are available for the shape factor of the cylindrical injection zone used to perform a field permeability test. Depending on the selected value, the resulting difference for hydraulic conductivity may reach 40% for long intake zones, and more than 100% for short intake zones. The commonly used shape factor is that given .
custom national control moisture meter
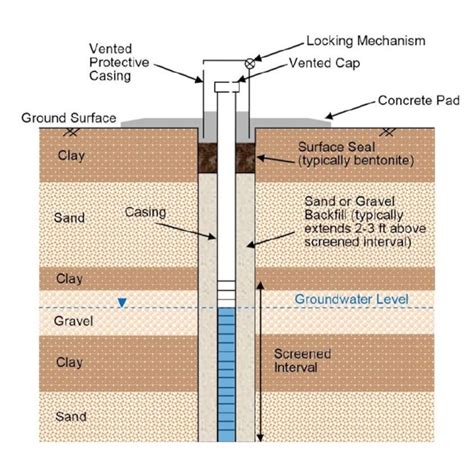
piezometer permeability chart
webRoblox is the ultimate virtual universe that lets you create, share experiences with friends, and be anything you can imagine. Join millions of people and discover an infinite variety of immersive experiences created by a global community! Roblox is ushering in the next generation of entertainment. Imagine, create, and play together with .
field permeability test in borehole|falling head permeability test astm